MIPI and USB cameras emerge as the frontrunners in the world of embedded vision. These cameras are indispensable tools across various industries, offering solutions for diverse imaging needs.
MIPI cameras, that use the Mobile Industry Processor Interface standard, are known for their low power consumption and high-speed data transfer capabilities, making them the ideal choice for AI vision devices, automotive systems, and industrial setups.
On the other hand, USB cameras, provide plug-and-play convenience and versatility. They cater to applications ranging from surveillance systems to video processing in embedded systems.
Despite their disparities, MIPI and USB cameras share a common trait of adaptability. This enables them to seamlessly integrate into various hardware environments. Their compatibility and acceptance across the industry underscore their pivotal roles in shaping the landscape of embedded vision technology.
This blog post takes a deeper look into MIPI and USB cameras, unraveling their defining features and learning how to choose between the two for your vision system.

What Are MIPI Cameras?
As stated earlier, MIPI cameras are a category of cameras that adhere to the standards set by the Mobile Industry Processor Interface (MIPI) Alliance, which ensures seamless interoperability between cameras and host processors.
Some of the advantages of MIPI cameras include:
- High-speed data transfer rate
- Low power consumption
- Compact form factor
- Highly flexible
The MIPI Alliance has developed several interfaces tailored for specific applications. These include MIPI Camera Serial Interface-1 (CSI-1), MIPI Camera Serial Interface-2 (CSI-2), and MIPI Camera Serial Interface-3 (CSI-3).
The CSI-1 interface was developed as an architecture to enable the connection between a camera and a host processor. It was used extensively for integrating cameras in embedded vision systems. In a way, CSI-1 laid the foundation for camera interfaces in the early iterations of camera-enabled systems. It was later replaced by the CSI-2 and CSI-3 standards.
The CSI-2 interface serves as the de facto standard for camera integration in embedded vision systems and other applications. It was released in 2005 and still reigns as the prominent interface for MIPI cameras. It supports multiple lanes for parallel data transmission, enabling high-bandwidth communication between cameras and host processors.
The CSI-3 is the latest interface with its first version introduced back in 2012, which was re-released in 2014 as v1.1. While CSI-3 serves as a high-speed, bidirectional interface, it failed to see widespread adoption in the embedded vision market. Thus, CSI-2 remains to be the most widely used interface for MIPI cameras to date.
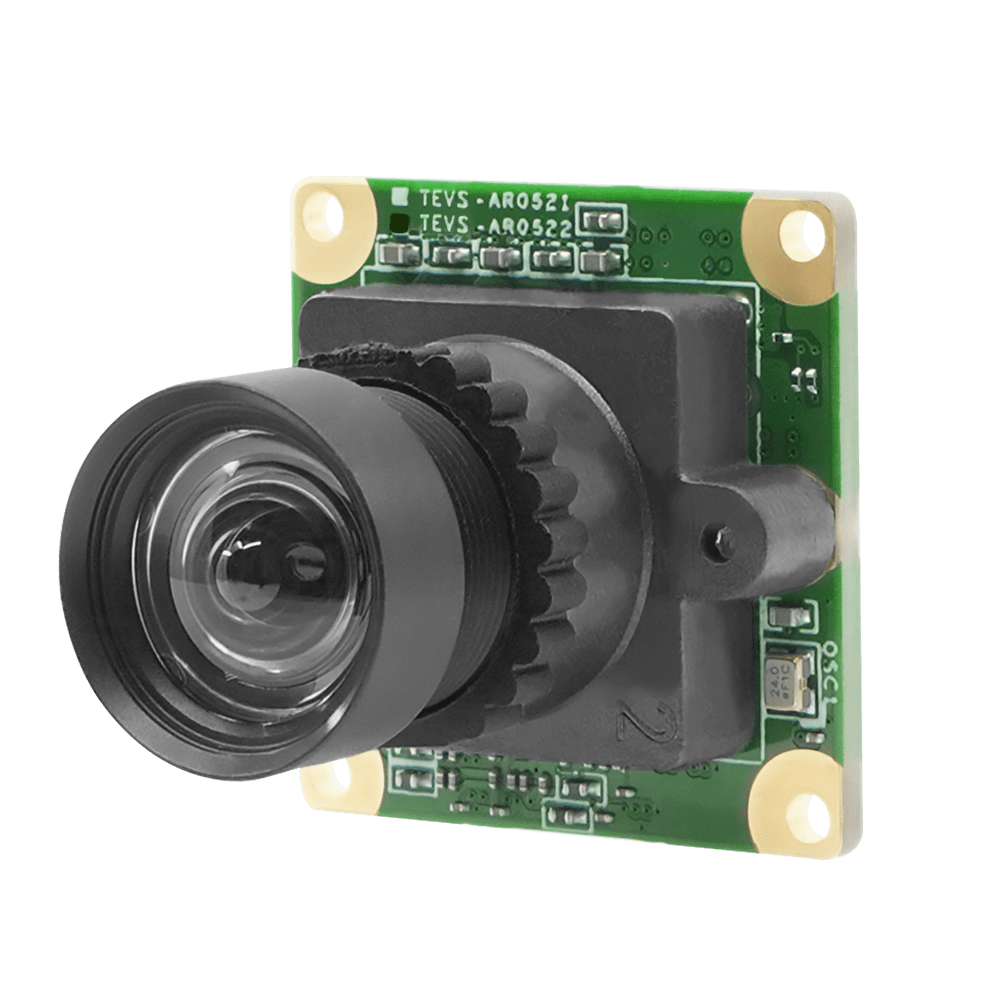
MIPI-CSI2 Sensor onsemi AR0522 5MP Color Rolling Shutter with ISP + 85 Degree M12 Lens with IR-Cut Filter
TEVS-AR0522-C-S85-IR
- Onsemi AR0522 5MP rolling shutter camera sensor with ISP
- Designed for low light and high dynamic range performance
- Convenient S-Mount (M12) interchangeable lens
- VizionViewer™ configuration utility
- VizionSDK for custom development
| Sensor | onsemi AR0522 |
| Shutter | Rolling |
| Megapixels | 5MP |
| Chromaticity | Color |
| Interface | MIPI-CSI2 |
| Module DFOV | 85.0° |

Key Embedded Vision Applications of MIPI Cameras
MIPI cameras find extensive usage across various embedded vision applications. This can be attributed to their high performance and power efficiency. Some key applications where MIPI cameras excel include:
- Automotive Systems: In automotive applications, MIPI cameras support advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS). They are also useful for number plate recognition in smart traffic systems.
- Industrial Imaging: MIPI cameras play a vital role in industrial automation, machine vision, and robotics. They help facilitate tasks such as quality inspection, object recognition, and defect detection with precision and reliability.
- Medical Imaging: Medical devices such as patient monitoring systems, drug delivery robots, lab equipment, and telehealth devices. The compatibility of MIPI cameras with compact processors like the NXP i.MX series makes the integration easy in medical devices.
What Are USB Cameras?
USB cameras are a class of cameras that utilize the Universal Serial Bus (USB) interface for connectivity with host systems. These cameras are designed to provide plug-and-play functionality.
This allows for straightforward installation and configuration without the need for additional hardware or complex setup procedures. Thus, they are often the first choice of cameras when it comes to an embedded vision system.
Some of the key features of USB cameras are:
- Ease of Installation: USB cameras are exceptionally user-friendly, requiring minimal setup effort. Most operating systems automatically detect and configure USB cameras without the need for specialized drivers or software.
- Versatility: USB cameras come in a wide range of configurations, from basic consumer-grade webcams to high-performance industrial cameras. This versatility allows users to choose the most suitable camera for their specific application requirements.
- Compatibility: USB cameras are universally compatible with a vast array of devices – all x86-based host systems. This broad compatibility ensures seamless integration into existing hardware environments without compatibility issues or interoperability concerns.
- Cost-Effectiveness: USB cameras are generally more affordable than their counterparts. This cost-effectiveness makes them an attractive option for budget-conscious users.

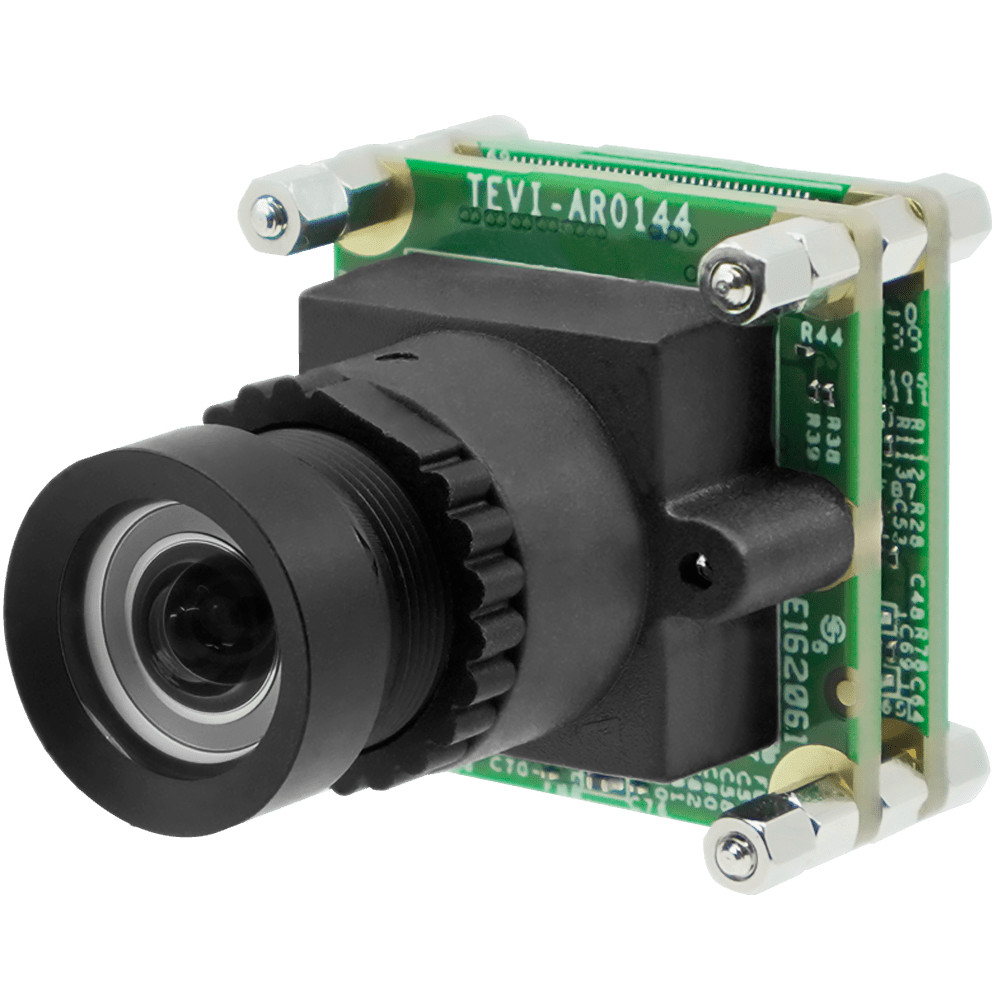
USB3 Type-C Camera with onsemi AR0144 1MP Color Global Shutter with Onboard ISP + 83 Degree M12 Lens with IR-Cut Filter + Incl. 1 Meter USB C Cable
VCI-AR0144-C-S83-IR
- onsemi AR0144 1MP Global Shutter Sensor
- S-Mount for Interchangeable Lenses
- UVC USB Type-C 5 Gbps Connector
- Plug & Play with Windows & Linux OS
- VizionViewer™ configuration utility
- VizionSDK for custom development
| Sensor | onsemi AR0144 |
| Shutter | Global |
| Megapixels | 1MP |
| Chromaticity | Color |
| Interface | USB3 |
| Module DFOV | 83.0° |
Key Embedded Vision Applications of USB Cameras
USB cameras find extensive usage across a wide range of embedded vision applications, owing to their ease of use, versatility, and affordability. Some key application areas include:
- Video Conferencing: USB camera modules are commonly used in video conferencing and telepresence systems, enabling remote communication and collaboration with high-quality video and audio.
- Surveillance systems: USB cameras serve as components in home and industrial surveillance and security systems. They can help identify potential threats autonomously and send automated alerts to security staff in case of a mishap.
- Telemedicine: USB cameras play a pivotal role in telemedicine applications, facilitating remote medical consultations and examinations. Healthcare professionals utilize USB cameras to capture high-resolution images and videos of patients’ conditions, allowing for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
- Industrial Automation: USB cameras are employed for a wide range of industrial applications, including inspection, quality control, and process monitoring. These cameras provide visual feedback to automated systems, enabling precise detection of defects, measurement of dimensions, and identification of anomalies in manufacturing processes.
MIPI Cameras vs. USB Cameras
A comparison between MIPI and USB cameras can be made by considering the following factors:
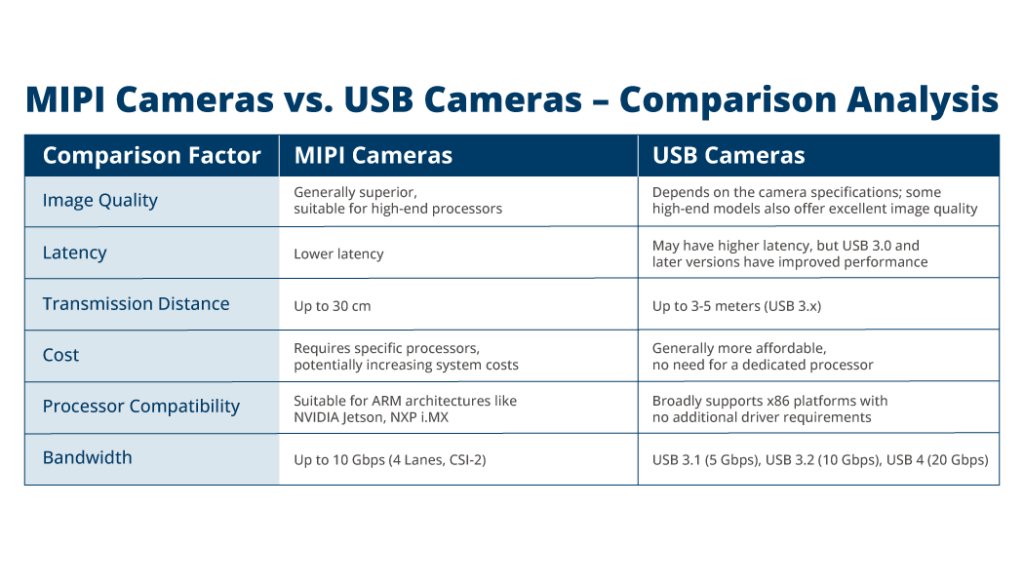
Image Quality
Image quality depends on a wide variety of factors and not just the interface. In general, MIPI cameras tend to have better image quality than USB cameras owing to their compatibility with high-end processing systems.
Latency
MIPI typically offers lower latency compared to USB. USB cameras may have higher latency due to additional data processing and protocol overhead. However, USB 3.0 and later versions have reduced this latency compared to USB 2.0.
Distance of Transmission
The MIPI interface is not recommended for use beyond 30 cm. USB cameras, on the other hand, can be used theoretically for a distance of 5 meters. Thus, USB cameras fare better in applications (such as robotic arms) that require longer transmission distances.
Cost
It is quite difficult to choose a winner when it comes to cost. The total cost of the system (including other components such as processors) also needs to be considered here. USB cameras tend to be cheaper in that context since they do not need specialized processors. At the same time, a high-end USB camera can result in higher costs compared to a low-end MIPI camera.
Host processor compatibility
One major advantage of USB cameras is their compatibility with various x-86 host systems, unlike MIPI cameras which are compatible with ARM-based processing platforms like NVIDIA Jetson. Plus, USB cameras also don’t need any additional drivers or complex setup procedures. Owing to this, product developers often prefer USB cameras for prototype development. If there is no flexibility when it comes to the host processor, the choice between the two will be primarily made based on the type of processor.
Bandwidth
MIPI offers high bandwidth suitable for transmitting high-resolution images and videos at high frame rates – 10 Gbps with 4 lanes with the CSI-2 interface. For USB cameras, the bandwidth may vary depending on the USB version. USB 3.0 and later versions offer higher bandwidth compared to USB 2.0, allowing for faster data transfer rates (5 Gbps for USB 3.1 and 10 Gbps for USB 3.2).
How to Choose Between MIPI and USB Cameras?
Selecting between MIPI and USB cameras requires careful consideration of several factors to ensure compatibility, performance, and suitability for the intended application. The factors include:
Host System
First and foremost, determine whether the host system supports or is compatible with the interface of the chosen camera. MIPI cameras work seamlessly with processors like TI Jacinto TDA4VM, NVIDIA Jetson, and NXP i.MX. On the other hand, USB cameras are compatible with x86-based processors. Ensure that the chosen camera interface aligns with the requirements and capabilities of the host system to avoid compatibility issues.
Distance of Transmission
USB cameras are more suited for long-distance transmission with the ability to practically attain a distance of transmission of up to 3 meters. MIPI cameras, on the other hand, are used in compact systems where the camera is placed close to the processor.
Bandwidth Required
MIPI cameras offer high-speed data transfer rates, with MIPI CSI-2 standard supporting up to 10 Gbps with four lanes. USB cameras also offer high-speed data transfer rates, with USB 3.1 offering 5 Gbps, USB 3.2 offering 10 Gbps, and USB 4 offering 20 Gbps. Thus, both MIPI and USB interfaces are suitable for high-bandwidth applications.
Multi-Camera Compatibility
Taking into consideration whether the vision application requires support for multiple cameras and how each interface handles multi-camera setups. USB cameras utilize a USB hub to connect multiple cameras to a single host system. MIPI cameras leverage multiple lanes and virtual channels to support multi-camera configurations. Evaluate the performance of both interfaces when connected with multiple cameras to ensure optimal performance and compatibility for the application.
TechNexion – Camera Solutions for New-Age Vision Systems
TechNexion offers a diverse portfolio of USB and MIPI cameras catering to various vision application needs. Our USB cameras are compliant with the UVC (USB Video Device Class) protocol and are built to seamlessly integrate with embedded vision systems. Our MIPI cameras are well-suited for vision systems that use ARM-based processors.
TechNexion’s cameras find applications in robots, drones, sports analytics devices, smart traffic systems, and more, providing reliable solutions for modern vision systems. Get in touch with us today to explore how our camera solutions can propel your vision projects to new heights.
Related Products
Get a Quote
Fill out the details below and one of our representatives will contact you shortly.